- Pancreatic Cysts during EUS-FNA
- Lesson 05/06
Mucinous cystadenoma
You may review the various image interpretation sets before doing some self training questions.
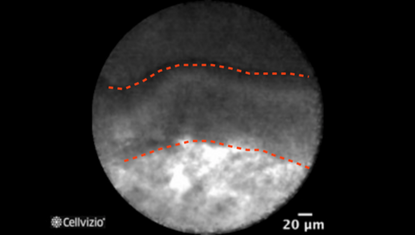
Epithelial border (first example)
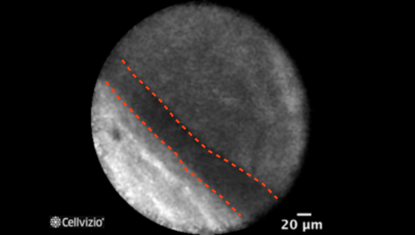
Epithelial border (second example)
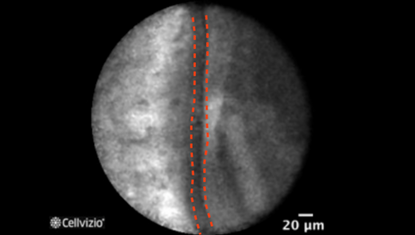
Epithelial border (third example)
PLAY THE TRAINING VIDEOS:
Organ: Pancreas
Investigated pathology: Pancreatic cyst
Probe type: AQ-FLEX 19
Laser wavelength: 488 nm
Courtesy: The CONTACT clinical trial, 2013
Organ: Pancreas
Investigated pathology: Pancreatic cyst
Probe type: AQ-FLEX 19
Laser wavelength: 488 nm
Courtesy: The CONTACT clinical trial, 2013
These criteria have been reported and assessed in clinical studies. Other criteria of interpretation might exist. Thus whenever possible, confirmatory evaluation via conventional histopathology or any other clinical information is recommended.
Pathology Correlation
What happens in a mucinous cystadenoma?
Correlation between a mucinous cystadenoma and endomicroscopy images:
Napoléon et al. (4) showed that pancreatic endomicroscopy can identify cytological elements in a mucinous cystadenoma.
Two distinct components are comprised in mucinous cystadenomas: a mucin-producing epithelium on a fibrous tissue containing ovarian-type stroma composed of densely packed spindle cells with some large blood vessels, seen at various depths. Since the epithelial border is parallel to the confocal plan of the miniprobe, Cellvizio should not be able to image the wall. However, folds may form in the cyst wall, which can be visualized on Cellvizio images. Indeed, on nCLE, the epithelial border is seen as a gray band delineated by a thin dark line. It usually appears as a single epithelial border in this case, which is different from the papillary projections in IPMNs. The ovarian-stroma is not clearly identified. Since the ovarian-stroma can be as 100 microns deep in the wall below the epithelial border, Cellvizio may not be able to image it.
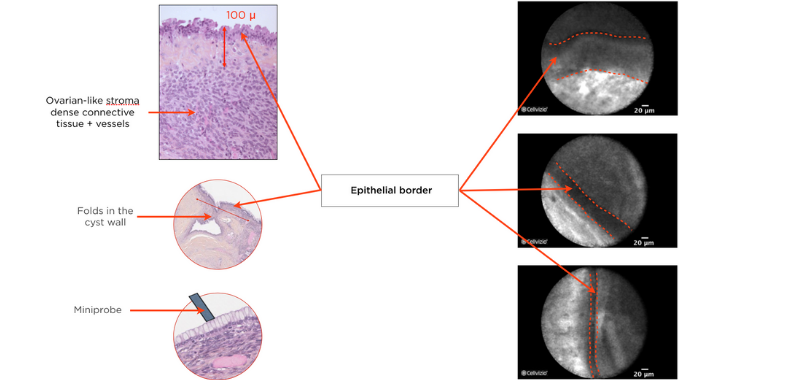
The epithelial border usually appears as a single epithelial border in MCN. It is different from the papillary projections in IPMNs, which appear as paired epithelial borders, surrounding a bright core.
References:
4) Napoleon B et al, In vivo characterization of pancreatic cystic lesions by needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) : proposition of a comprehensive nCLE classification confirmed by an external retrospective evaluation, Surg Endosc. 2015 Oct 1

