- Pancreatic Cysts during EUS-FNA
- Lesson 04/06
Pseudocyst
You may review the various image interpretation sets before doing some self training questions.
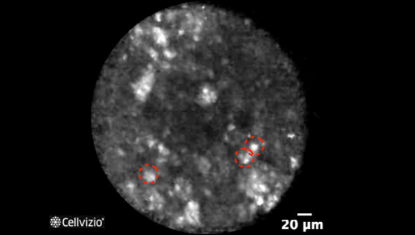
Inflammatory cells: Field of bright particles
PLAY THE TRAINING VIDEOS:
Organ: Pancreas
Investigated pathology: Pancreatic cyst
Probe type: AQ-FLEX 19
Laser wavelength: 488 nm
Courtesy: The CONTACT clinical trial, 2013
Organ: Pancreas
Investigated pathology: Pancreatic cyst
Probe type: AQ-FLEX 19
Laser wavelength: 488 nm
Courtesy: The CONTACT clinical trial, 2013
These criteria have been reported and assessed in clinical studies. Other criteria of interpretation might exist. Thus whenever possible, confirmatory evaluation via conventional histopathology or any other clinical information is recommended.
Pathology Correlation
What happens in a pseudocyst?
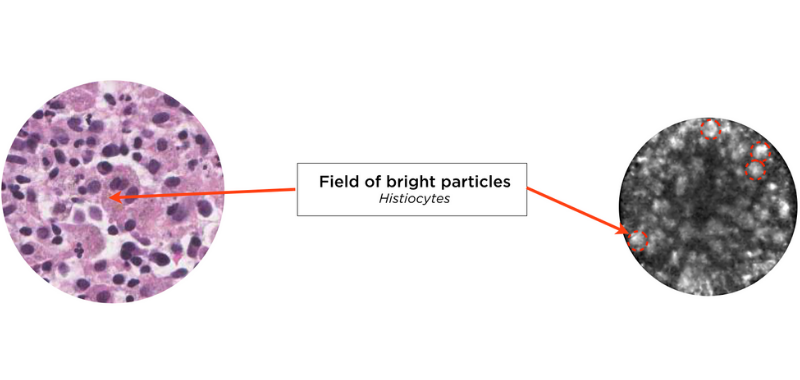
Correlation between a pseudocyst and endomicroscopy images:
Napoléon et al. (4) showed that pancreatic endomicroscopy can identify cytological elements in a pseudocyst. A pseudocyst is a fibroinflammatory tissue surrounding necrotic adipocytes, without epithelial lining. The wall can be either actively inflamed tissue with necrotic debris, or a densely hyalinized collagen. In this case, Cellvizio does not enable to image the wall.
Instead, endomicroscopy images reveal a field of bright particles measuring between 10 and 40 microns, which correlate with a mix of inflammatory cells, with the presence of bright particles corresponding to histiocytes.
References:
4) Napoleon B et al, In vivo characterization of pancreatic cystic lesions by needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) : proposition of a comprehensive nCLE classification confirmed by an external retrospective evaluation, Surg Endosc. 2015 Oct 1

